Population in Africa: Growth, Challenges, and Future Projections
Explore Africa's population trends, growth rate, challenges, and future projections. Understand the impact of urbanization, economy, and policies on Africa's demographics."
POPULATION IN AFRICA
Population refers to the number of people living in a given area. It relates to the way human settlements have been distributed in a given area.
Population is unevenly distributed in Africa. The most populous countries are Nigeria, Egypt, South Africa, Ethiopia and Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).Africa ranks as the second-largest continent in both size and population, following Asia. Spanning approximately 30.3 million square kilometers, including surrounding islands, it makes up 20% of the Earth's landmass and 6% of its total surface. As of 2021, Africa's population neared 1.4 billion, representing roughly 18% of the global population.
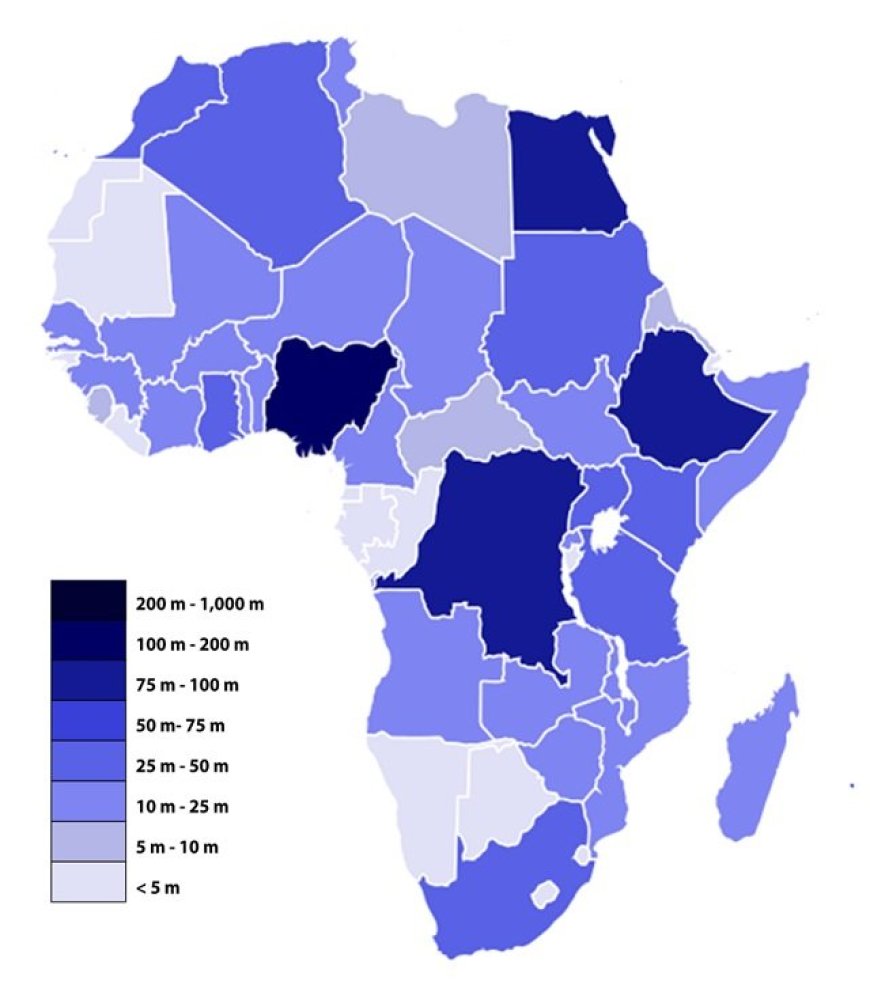
SKETCH MAP OF AFRICA SHOWING POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
When you look at a population distribution map of Africa above, you find out that in some parts of Africa such as the Nile delta of Egypt, the Niger delta in Nigeria, Johannesburg in South Africa and Kinshasa in the DRC, there are vast numbers of people. This means that the population density is high. In such areas there is little land available per person and the end result is congestion. Such congestion is associated with various problems such as inadequate housing leading to development of slums, traffic jams and easy spread of diseases. On the other hand, one can also note that from the very map that there are large areas which are sparsely populated such as the interior areas of Libya, Algeria, Mali, Morocco and Namibia. Such low population poses an obstacle to the development of such areas.
FACTORS INFLUENCING POPULATION DISTRIBUTION IN AFRICA
1. Climate. Areas with hot temperatures and heavy rainfall which is well distributed throughout the year such as the coastal areas of South Africa, Pretoria, Nigeria, and Nile Valley have attracted dense population while areas with hot and little rainfall like Sahara, Kalahari and Namib Desert have sparse population because they support the growth of few crops.
2. Soils. Areas with fertile soils such as along Eastern coast of South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia highlands, Niger Delta have attracted dense population while areas of light and sharp shallow of semi-desert have sparse population.
3. Water. Presence of water for domestic and industrial use from Orange river, Congo River has led to dense settlement as compared to areas with scarcity of water E.g. in Sahara deserts.
4. Vegetation. Thick forested areas like Congo basin have sparse population due to tsetse fly infestation, remoteness as compared to thin forested areas, for example in the northern Africa
5. Relief. Steep slopes of African highlands such as Drakensburg, Atlas, Ethiopia highlands have sparse population due to landslides and steep slopes while in gentle slopes have attracted dense settlement due to the deep fertile soils and vegetation.
6. Minerals. Mining areas like Rand, Kimberly of South Africa, Zambia, copper belt, oil in Niger Delta have attracted dense population.
7. Government policy. Government policy such as the development of the Nile valley, coastal ports of South Africa like Cape Town and Durban have led to dense population. Areas that have been gazette as game parks have sparse population.
8. Urbanisation. Urban centers like Johannesburg, Pretoria, Cairo, Abuja and Lagos in Nigeria offer social services and employment opportunities and so they are dense populated unlike rural areas.
9. Accessibility. Accessibility in Natal province , south Africa, Nile valley in Egypt with modern roads and railway lines have favoured trade and easy mobility hence having dense population un like remote areas.
10. Historical factors. The influence of ancient kingdom such as Zulu in South Africa, Alexander pharaoh, Ibo in Eastland, Yoruba kingdom in Nigeria attract settlement.
POPULATION DENSITY
Population density This refers to the average number of people living in a unit area or land. It is calculated by dividing the total number of population in a country by total land area of that country.
PD=Total Population
Total land area
Exercise:
Table 1: Population of selected African Countries (2012).
|
Country |
Total Population in millions |
Total Land Area (1000 km2 ) |
|
Angola Cameroon Gabon Zambia Liberia |
20.8 21.7 1.6 14.1 4.2 |
1,246.7 475.4 267.7 752.6 111.4 |
Adapted: 2014 World Development Indicators: The World Bank Washington D.C. pp. 12-16.
(a) Draw a bar graph to represent the population of the countries shown in the table above.
|
|
|
FACTORS WHICH HAVE LED TO RAPID POPULATION INCREASE IN AFRICA
1. High birth rate due to high fertility of the women in many countries especially in Nigeria, Egypt, Ethiopia where a woman on average gives birth to 5 to 7 children leading to large population size.
2. Improved medical services which leads to decline in death rates among the population for example wide spread immunisation of killer diseases like measles, polio, hepatitis leading to rapid population.
3. Early marriages among the youth due to high rate of school dropout giving rise to longer periods of childbirth thus high population size.
4. Immigration from other countries like Somalia, DRC leading to a large population size.
5. Polygamous marriages encouraged by Muslims especially in Nigeria and Egypt who marry more than one wife leading to production of more children thus large population size.
6. Improved nutrition as a result of increased food production to feed the increasing population led to rapid population increase in Africa most especially in Nigeria, South Africa and Egypt.
7. Ignorance of family planning methods by most people in Nigeria, Ethiopia and Egypt lead to the production of more children than the available resources hence rapid population increase in Africa.
8. Improved sanitation due to increased incomes that have increased the living standards of people leading to low incidences of disease outbreak thus large population size.
9. Religious factors where Muslims marry more than one wife thus producing many children while Christians are negative about birth control methods thus a large population size.
10. Traditional beliefs/ cultural values of having many children especially for security, prestige, wealth and continuation of the family lineage thus large population size.
EFFECTS OF RAPID POPULATION INCREASE ON THE ENVIRONMENT IN AFRICA
Negative effects of large population
1. Shortage of land leading to land disputes among the people especially in rural areas of Africa.
2. Land degradation due to over cultivation of land to increase food production to feed the increasing population resulting into low productivity of land leading to viscous circle of poverty.
3. Deforestation leading to reduced rainfall and accelerating rate of soil erosion
4. Encroachment on the marginal lands such as forests, wetlands, game parks and game reserves hence affecting other economic activities such as tourism.
5. Shortage of food leading to reduced food security hence starvation and famine.
6. It leads to poverty due to low savings and low investments.
7. Increased pressure on social economic services such as roads, schools, hospitals among others.
8. It leads to inadequate accommodation or housing leading to development of slums with associated problems such as murder, prostitution among others.
9. It leads to rapid spread of epidemic diseases for example cholera, typhoid and STDs due to congestion.
10. It leads to unemployment leading to many problems such as high crime rates like prostitution, murder and pick-pocketing.
Positive effects of large population
1. Large population provides a large market for agricultural and industrial goods as well as services leading to increased production.
2. It provides cheap labour to do different business enterprises and to work in different sector s such as agriculture, mining, forestry, tourism among others which leads to increased output of goods and services.
3. Increased source of revenue from taxation for the development of infrastructures like roads, schools, hospitals market structures among others.
4. Large population attracts socio-economic infrastructures from the government especially schools, hospitals, water supply, roads among others.
5. It encourages innovativeness since jobs are scarce more especially in technology, business and agriculture so as to earn income.
6. Dense population has contributed to the growth of urban centres such as Abuja, Lagos, Kano, Addis Ababa, Cairo, with associated infrastructures such as roads schools and health centres.
7. Provides large force/ army which can defend the country in case of war.
STEPS BEING TAKEN TO CONTROL POPULATION INCREASE IN AFRICA
1. Family planning methods are being encouraged so as to control high birth rates.
2. Encouraging outward migration from the densely populated regions.
3. Setting up resettlement schemes where people are transferred from densely populated regions to areas to low population concentration.
4. Educating the masses to change their traditional attitude of having large families.
5. Vertical expansion to towns and cities through the building of storied houses so as to increase accommodation facilities.
6. Availing more services such as health centres and school to match the increasing population.
7. Encourage the educating of girls to higher levels so as to avoid early marriages.
8. Industrialisation to reduce over dependence on the land and to create employment for the increasing population.
9. Exploitation of existing natural resources so as to create land for agricultural activities to increase food production.
10. Discouraging polygamy among the Muslims by encouraging monogamy.
CASE STUDY: POPULATION IN NIGERIA
Nigeria is one of the highest populated countries in Africa with a population of 197,844,437 and the total land area is 923768km2. Nigeria population clock and it is ranked number seven in the world. Nigeria is generally split between Christianity and Islam. Most Nigerian are Muslims.
Dense settlements are found along the coastal areas such as Lagos, Port Harcourt, Oyo, Onitsha, and Enugu.
Large population is concentrated in towns like Kano, Sokoto, Abuja, and Niger delta.
MAP OF NIGERIA SHOWING POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
FACTORS WHICH HAVE LED TO A HIGH POPULATION DENSITY IN NIGERIA (NIGER DELT)
1. Constant or permanent source of water from river Niger for irrigation for irrigation and navigation attract large population.
2. Availability of the fertile alluvial soils brought down by river Niger during times of floods. Farmers have been attracted to the Niger delta leading to a large population.
3. Gentle landscape which allows the construction of canals and irrigation channels hence attracting large population for agricultural activities.
4. Extensive land for perennial agriculture leading to increased food production thus attracting large population.
5. Presences of many or numerous industries along the Niger delta to process agro-based products have attracted large population.
6. Presence social amenities like piped water, health, education in towns and cities have attracted large population in Lagos, Onitsha and Port Harcourt.
7. Availability of a variety of transport and communication systems by water road and railway thus attracting large population for easy transportation of goods and services.
8. Presence of a variety or numerous minerals such as iron ore, petroleum, coal and tin has attracted many people in the area to carry out mining activities.
9. Political stability along the Niger delta has attracted large population to carry out many activities without interruption.
10. Presence of extensive or prosperous fishing grounds that has led to extensive fishing attracted large population along the Niger delta.
CHALLENGES FACED BY PEOPLE LIVING IN DENSELY POPULATED AREAS IN NIGERIA
1. Overcrowding or congestion of people leading to easy spread of diseases and poor sanitation.
2. Strain on the social amenities such as hospitals, schools, roads leading to break down.
3. Poor sanitation leading to easy spread of diseases such as cholera, typhoid etc.
4. Over exploitation of natural resources like minerals and forests leading to exhaustion and depletion respectively.
5. Shortage of food leading to high expenditure on imported food.
6. Shortage of land for settlement and agriculture leading to low crop production hence famine and starvation.
7. High rates of unemployment leading to high crime rates such as murder, smuggling, pick-pocketing and prostitution.
8. Pollution of the environment like water, air and land leading to poor health and easy spread of diseases.
9. Development of slums due to inadequate accommodation leading to poor sanitation, moral decay among others.
10. Political unrest leading to loss of life and property.
11. Destruction of vegetation cover to create land for agriculture leading to loss of bio-diversity.
STEPS BEING TAKEN TO ADDRESS THE CHALLENGES FACED BY PEOPLE IN DENSELY POPULATED AREAS
1. Building sky scrapers to effectively utilise the available space.
2. Encouraging out-ward migration to less densely populated areas.
3. Practicing modern methods of agriculture to maintain soil fertility and productivity for example use of fertilizers, crop rotation mixed farming among others.
4. Importing food to supplement domestic agricultural production.
5. Diversifying the economy by promoting tourism, industrialisation, mineral exploitation and processing.
6. Encouraging use of population control measures such as use of family planning.
7. Mass awareness and education programmes on dangers of high population.
8. Employing security personnel or strengthening security in the area to control crimes.
9. Promoting tree planting along the Niger delta and Niger valley to control flooding on the lower section.
10. Developing rural areas through rural electrification, constructing modern roads, schools and hospitals so as to attract people in rural areas.
CASE STUDY: POPULATION IN EGYPT
Egypt is located in the North East corner of Africa. Egypt lies in a key position. It has a coastline on the Mediterranean in the north and red sea in the East. Egypt is bordered by Libya to the West, Sudan to the South and Israel and Gaza strip to the North East, the Gulf of Aqaba to the East.
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION IN EGYPT
Currently, Egypt has a population of 100,103,206 people according to Egypt clock 2018 with total land area of 1,002,450km2 and population density of 99.13 per km2. It ranked fourteen in the world. Egypt has a highly uneven population distribution. Dense settlements are concentrated along the Nile valley like Qena, Giza, Cairo, Alexandria, Asyut, Nile delta especially Tanta, Helwan, North eastern coast near both the Red and Mediterranean seas at Port Said.
SKETCH MAP OF EGYPT SHOWING POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
FACTORS WHICH HAVE LED TO A HIGH POPULATION DENSITY IN EGYPT (NILE VALLEY AND NILE DELTA)
1. Constant or permanent source of water from river Nile for irrigation for irrigation and navigation attract large population.
2. Availability of the fertile alluvial soils brought down by river Nile during times of floods. Farmers have been attracted to the Nile valley and Nile delta leading to a large population.
3. Gentle landscape which allows the construction of canals and irrigation channels hence attracting large population for agricultural activities.
4. Extensive land for perennial agriculture leading to increased food production thus attracting large population.
5. Presences of many or numerous industries along the Nile valley and the Nile delta to process agro-based products have attracted large population.
6. Presence social amenities like piped water, health, education in towns and cities have attracted large population in Cairo, Port Said and Alexandria.
7. Availability of a variety of transport and communication systems by water road and railway thus attracting large population for easy transportation of goods and services.
8. Presence of a variety or numerous minerals such as iron ore, salt, phosphates, manganese and oil has attracted many people in the area to carry out mining activities.
9. Political stability along the Nile valley has attracted large population to carry out many activities without interruption.
10. Presence of extensive or prosperous fishing grounds that has led to extensive fishing attracted large population along the Nile delta.
11. Early settlement along the Nile valley and delta by the Greeks attracted large population.
CHALLENGES FACED BY PEOPLE LIVING IN DENSELY POPULATED AREAS IN EGYPT
1. Overcrowding or congestion of people leading to easy spread of diseases and poor sanitation.
2. Strain on the social amenities such as hospitals, schools, roads leading to break down.
3. Poor sanitation leading to easy spread of diseases such as cholera, typhoid etc.
4. Over exploitation of natural resources like minerals and forests leading to exhaustion and depletion respectively.
5. Shortage of food leading to high expenditure on imported food.
6. Shortage of land for settlement and agriculture leading to low crop production hence famine and starvation.
7. High rates of unemployment leading to high crime rates such as murder, smuggling, pick-pocketing and prostitution.
8. Pollution of the environment like water, air and land leading to poor health and easy spread of diseases.
9. Development of slums due to inadequate accommodation leading to poor sanitation, moral decay among others.
10. Political unrest leading to loss of life and property.
11. Destruction of vegetation cover to create land for agriculture leading to loss of bio-diversity.
STEPS BEING TAKEN TO ADDRESS THE CHALLENGES FACED BY PEOPLE IN DENSELY POPULATED AREAS (NILE DELTA AND NILE VALLEY
1. Building sky scrapers to effectively utilise the available space.
2. Encouraging out-ward migration to less densely populated areas.
3. Practicing modern methods of agriculture to maintain soil fertility and productivity for example use of fertilizers, crop rotation mixed farming among others.
4. Importing food to supplement domestic agricultural production.
5. Diversifying the economy by promoting tourism, industrialisation, mineral exploitation and processing.
6. Encouraging use of population control measures such as use of family planning.
7. Mass awareness and education programmes on dangers of high population.
8. Employing security personnel or strengthening security in the area to control crimes.
9. Promoting tree planting along the Niger delta and Niger valley to control flooding on the lower section.
10. Developing rural areas through rural electrification, constructing modern roads, schools and hospitals so as to attract people in rural areas.
FACTORS WHICH LED TO THE LOW POPULATION DENSITY IN EGYPT
1. Unreliable rainfall of less than 250mm per annum discourages agriculture and settlements.
2. Availability of infertile, thin and unproductive soils leading to low production and are easily eroded by wind.
3. Scarcity or shortage or limited surface water in the desert landscape led to population density.
4. Low soil water content since the soils are sandy and porous or low water retention capacity.
5. Strong winds causing desert storms that destroy property and infrastructures such as houses led lo low population density.
6. Remoteness or inaccessibility. The area is poorly served with transport and communication routes hence discouraging settlements.
7. High rates of evaporation due to extremely hot temperatures of between 350 and 400 discourage settlements on such areas.
8. Limited economic activities since there are no valuable minerals, agriculture and industry leading to low population density.
9. Presence of numerous sand dunes which disrupt transport and communication leading to low population.
10. High incidences of pests and diseases such as locusts that destroy crops, forests leading to settlement hence low population density.
PROBLEMS FACED BY PEOPLE LIVING IN THE SPARSELY POPULATED AREAS
1. High costs of establishment infrastructures such as roads, school and hospital.
2. Low food productivity leading to famine, malnutrition and death.
3. Low standards of living due to limited economic activities.
4. Inaccessibility of most areas leading to slow movement of goods and people.
5. Pests such as locusts which destroy vegetation and crops.
6. Diseases like eye infection, flue and cough leading to suffering and death.
7. Strong desert storms leading to destruction of infrastructures, property and lives.
8. Shortage of labour leading to under development of the various economic activities like mining.
9. Shortage of water leading to death of people and animals
10. Low tax base due to low population density in the area.
11. Limited market for goods and services in the area due to population.
12. Under utilisation of the available due to low population density leading to low tax base.
MEASURES BEING TAKEN TO CONTROL THE PROBLEMS FACED BY SPARSELY POPULATED AREAS IN AFRICA
1. Provision of water from underground sources from river Nile, Niger to the drier areas and sinking of borehole.
2. Application of organic manure in the desert areas to improve soil fertility.
3. Planting of quick maturing crops varieties to prevent the problems of famine, malnutrition and starvation.
4. Use of irrigation farming to supplement on the limited rainfall.
5. Setting development projects like settlement projects and industries to encourage immigration.
6. Diversification of economic activities to create more employment opportunities and widening the tax base.
7. Afforestation or tree planting to improve on the vegetation cover to modify the climate of the area.
8. Growing of drought resistant crops and pastures to control the death of animals.
9. Importation of food from other countries to supplement on what can be produced.
10. Arial spraying of pests and diseases using chemical to control pests and diseases.
11. Importation of labour from other countries to work in the different economic activities.










































