How Do Smartphones Work The Science Inside Your Pocket
Explore the technology behind smartphones and how they function. Learn about processors, touchscreens, sensors, and wireless communication that power the device in your pocket.
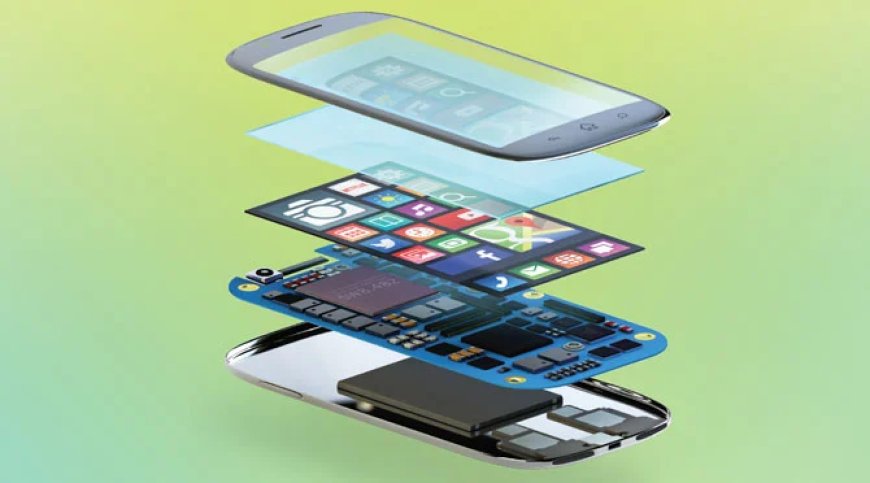

Smartphones, essential devices in contemporary society, are compact communica- tion and computing tools that have revolutionized the way individuals connect, work, and engage with the world. Originating in the early 1990s with the introduction of the IBM Simon, often regarded as the first smartphone, these devices have evolved significantly, integrating features such as touchscreens, internet connectivity, and multifunctional applications that blend personal and professional capabilities.[1][2] This technological advancement has spurred a global smartphone market, impacting daily life across various demographics.
The evolution of smartphones can be marked by significant milestones, particularly the launch of the iPhone in 2007, which set new standards for design and functionality and catalyzed a competitive landscape among manufacturers.[3] The subsequent introduction of Android as an open-source operating system further diversified the market, enabling a wide range of manufacturers to innovate and cater to various consumer needs.[3] Today, smartphones are equipped with advanced hardware and software components, including powerful processors, high-resolution displays, and sophisticated operating systems, allowing for seamless multitasking and high-quality multimedia experiences.
Despite their widespread adoption and undeniable benefits, smartphones have not been without controversy. Issues such as digital addiction, privacy concerns, and the blurring of boundaries between personal and professional life have emerged as significant societal challenges linked to smartphone usage.[4][5] The impact of smart- phones on communication dynamics, economic practices, and social interactions continues to be a topic of ongoing debate, raising questions about their long-term implications on human behavior and relationships.[4][6] As technology advances, the future of smartphones promises further innovations, including enhancements in connectivity and device design, shaping the next chapter in mobile technology.
History of Smartphones
The history of smartphones is a testament to the rapid evolution of mobile communi- cation technology, marking significant milestones that have transformed the way we connect, work, and entertain ourselves. The journey began in the early 1990s with the introduction of the IBM Simon Personal Communicator in 1994, often hailed as the first smartphone. This innovative device combined the functionalities of a mobile phone with those of a personal digital assistant (PDA), featuring a touchscreen in- terface, email capabilities, and rudimentary applications like a calendar and address book[1][2].
The Rise of Early Smartphones
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw a surge in the development of smartphones. Notably, in 2000, the Ericsson R380 was released, recognized as the first true smartphone, offering a monochrome touchscreen and support for mobile internet browsing[1]. During this period, companies like Palm and Handspring were also innovating, introducing devices such as the Palm Pilot and Handspring VisorPhone, which further blurred the lines between mobile phones and PDAs.
In 2002, Research In Motion (RIM) launched the BlackBerry 5810, which integrated email and web browsing capabilities with a traditional mobile phone form factor, paving the way for the proliferation of mobile communication tools in the business sector[1]. This period marked the initial blending of productivity and communication, setting the foundation for future advancements.
The Smartphone Revolution
The early 2000s marked a turning point, with the introduction of 2G and 3G tech- nologies that transformed phones into gateways to the Internet. As phones evolved into mini-computers, capabilities expanded to include web browsing, video calls, and the downloading of digital content[3]. The climax of this evolution came with Apple's unveiling of the iPhone in 2007, which introduced a sleek design, a robust operating system, and a user-friendly touchscreen interface[3]. This innovation not only redefined the smartphone but also sparked a competitive race in the mobile industry.
Simultaneously, Google’s introduction of the Android operating system further fueled innovation by providing an open-source platform that enabled diverse smartphone manufacturers to customize and develop their devices, increasing competition and variety in the market[3]. The fusion of functionality and design during this period helped establish smartphones as indispensable tools for everyday life.
Integration of Services
Smartphones have transformed interactions by integrating various forms of commu- nication into multifunctional devices. This includes voice calls, text messaging, and
Internet-Based Communication Tools
In addition to smartphones, the adoption of internet-based communication tools has grown exponentially. Platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack have become integral to daily interactions, particularly in professional settings. These tools enable real-time collaboration, facilitating meetings, information sharing, and seamless teamwork across geographical boundaries[9][7].
Recent Developments and Future Prospects
As smartphones have continued to evolve, new technologies have emerged, in- cluding advancements in screen technology and camera capabilities. Early mobile phones had basic screens, whereas modern smartphones feature high-resolution OLED displays, enabling immersive experiences[2]. The integration of cameras has transformed how people capture memories, with today's devices rivaling dedicated cameras in quality.
Looking ahead, the future of smartphones promises even more innovations. Emerging technologies such as 5G connectivity will deliver faster internet speeds and lower latency, paving the way for enhanced experiences in augmented reality, virtual reality, and cloud gaming. Additionally, the development of foldable smartphones with flexible displays is set to revolutionize device design and user interaction[1][2].
Hardware Components
Smartphones are sophisticated devices that rely on a range of hardware components to deliver functionality and performance. These components can be broadly catego- rized into several key areas, each contributing to the device's overall operation and user experience.
Key Hardware Components
Processor (CPU)
The central processing unit (CPU) is often referred to as the brain of the smart- phone. It is responsible for executing instructions, processing data, and managing the flow of information within the device. The CPU runs the operating system and applications, making it crucial for the overall performance and responsiveness of the smartphone[10][11]. Modern CPUs also incorporate advanced architectures that support multitasking and enhance processing efficiency, allowing users to perform complex tasks without noticeable lag[12].
Memory
Memory in smartphones typically consists of two main types: random access memory (RAM) and storage. RAM is used for temporary data storage while applications are running, facilitating quick access to active tasks. In contrast, storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), hold data permanently, including apps, images, and user files[13][14]. The amount of RAM and storage directly affects a smartphone's ability to handle multiple applications and store large amounts of data.
Display
The display is a critical hardware component that serves as the primary interface for user interaction. It is responsible for rendering graphics and text, utilizing technologies such as LCD or OLED to deliver vibrant visuals and responsive touch capabilities[15]. High-resolution displays enhance the overall user experience, especially for tasks such as gaming and multimedia consumption.
Battery
The battery is essential for powering the smartphone, providing the energy necessary for all functions and features. Modern smartphones often use lithium-ion batteries, which offer a balance of performance, longevity, and efficiency. Battery life is a significant consideration for users, influencing how long the device can operate before needing a recharge[13].
Camera
Smartphone cameras have evolved to become powerful tools for photography and videography. They typically include multiple lenses and sensors that enable various shooting modes and high-quality image capture. The image processing unit (ISP) within the smartphone processes data from the camera to produce clear and vibrant images and videos[12]. This functionality has made smartphones a primary device for capturing and sharing moments.
Antenna
The antenna is a vital component that facilitates communication between the smartphone and network towers. Various types of antennas are used, including microstrip-based patch antennas, which are popular due to their compact size and multi-band capabilities. These antennas support a range of technologies, including GSM, CDMA, LTE, and Bluetooth, ensuring reliable connectivity for voice and data transmission[15][13].
Additional Components
Other important hardware components include speakers, microphones, and sensors (such as accelerometers and gyroscopes), which enhance user interaction and enable various functionalities, such as voice commands and motion detection. These
Software Components
Smartphones rely heavily on various software components that work in concert with the hardware to deliver a seamless user experience. The primary software component of a smartphone is the mobile operating system (OS), which acts as the backbone for all other applications and functionalities. Popular mobile operating systems include iOS from Apple, Android from Google, and Huawei's HarmonyOS, each providing an interface that allows users to interact with the device’s hardware and run applications efficiently[16][17].
Mobile Operating Systems
Mobile operating systems manage the essential functions of smartphones, including running applications, controlling memory, and managing network connectivity. They offer an intuitive user interface that presents icons and tiles, enabling users to access various features quickly. In addition to managing applications, mobile OSes handle connectivity, allowing devices to connect to cellular networks and Wi-Fi[16][17].
Key Features
Mobile operating systems come with a multitude of features designed to enhance user interaction and utility:
Application Management: OSes facilitate the installation, execution, and manage- ment of apps, providing users access to a wide range of functionalities, from produc- tivity tools to games[18][17].
Network Connectivity: They manage the connection to wireless networks, allowing users to make calls, send messages, and browse the internet[17][19].
User Interface: Mobile operating systems provide customizable interfaces that enable users to personalize their devices according to their preferences[20][21].
Native Applications: Most mobile OSes include built-in applications for email, calen- dar management, and navigation, which rely on the device's hardware to function properly[17][19].
Application Software
Beyond the operating system, smartphones run various application software, cate- gorized into several types:
System Software: This includes the OS itself, which manages hardware resources and provides the environment for application software to run[14][21].
Utility Software: These background programs perform maintenance tasks, such as antivirus functions and system optimization[14][21].
Application Software: This encompasses user-facing applications like web browsers, social media platforms, and productivity tools, which facilitate day-to-day tasks and entertainment[14][21].
Hardware-Software Interaction
The interaction between software and hardware is critical to the functionality of smartphones. The OS serves as an intermediary between the user and the hard- ware, translating user commands into actions executed by the smartphone's internal components, such as the CPU and GPU[20][21]. This synergy not only enables tasks like multimedia processing and gaming but also enhances personalization and adaptability, allowing users to create a unique digital environment tailored to their needs[21].
Communication Technologies
As technology evolves, communication methods are constantly being refined to meet the needs of diverse populations. This section explores various technological innovations that have emerged to facilitate seamless interaction across different regions and communities. These advancements, including the rise of smartphones and internet-based tools, play a crucial role in enhancing connectivity and ensuring efficient exchanges[9].
Historical Context
The journey of communication technologies can be traced back to significant mile- stones such as the telegraph, which revolutionized long-distance correspondence in the 19th century, followed by the telephone that introduced real-time voice communi- cation[7]. The advent of radio and television in the 20th century further shaped collec- tive experiences and cultures, laying the groundwork for the diverse communication options available today.
The Smartphone Revolution
Integration of Services
Smartphones have transformed interactions by integrating various forms of commu- nication into multifunctional devices. This includes voice calls, text messaging, and internet access, leading to the emergence of advanced handheld tools that have reshaped personal and professional communication[7]. Key features such as instant messaging and social media platforms have made communication more immediate and fluid, influencing behaviors and expectations in both spheres[7][8].
Internet-Based Communication Tools
In addition to smartphones, the adoption of internet-based communication tools has grown exponentially. Platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack have
become integral to daily interactions, particularly in professional settings. These tools enable real-time collaboration, facilitating meetings, information sharing, and seamless teamwork across geographical boundaries[9][7].
Innovations in Communication
Another noteworthy trend is the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) in com- munication technologies. AI-driven applications, such as virtual assistants and auto- mated translation services, have made significant strides in breaking down language barriers and enhancing understanding among individuals from different linguistic backgrounds. These innovations not only streamline communication but also foster inclusivity and accessibility[9].
The smartphone's capabilities extend beyond basic functions; they utilize various technologies such as Near Field Communication (NFC) for data transfer and pay- ments, as well as Bluetooth for connecting with other devices[13]. These features collectively enhance the user experience and enable a range of functionalities that redefine modern communication.
Data Processing and Storage
Smartphones are sophisticated devices that integrate various components to man- age data processing and storage efficiently.
Data Processing
At the core of a smartphone's functionality is its operating system, which processes data, assigns CPU time, and manages memory allocation to handle input from various applications. This allows for multitasking, where multiple applications can run simultaneously by allocating CPU time slices to each application, creating the illusion of concurrent operation[14]. The central processing unit (CPU) serves as the "brains" of the smartphone, executing code for the operating system and applications, while the graphics processing unit (GPU) handles graphics-related tasks, rendering visual elements on the display[12]. Additionally, specialized processors like the image processing unit (ISP) and neural processing unit (NPU) are utilized to enhance specific functions, such as camera operations and machine learning tasks[12].
Storage Management
Data storage in smartphones is typically managed through a combination of in- ternal and external storage options. Internal storage, often built on flash memory technology, holds the operating system, applications, photos, and other user data. Common types of internal memory include LPDDR3, LPDDR4, and LPDDR4X, with the latter two providing faster performance[22].
Smartphones also leverage cloud storage solutions, allowing users to store and access data remotely, thereby reducing reliance on physical storage[23]. This in- tegration enables efficient data management, where users can back up their data
securely and access it from multiple devices[1]. Furthermore, the interaction between hardware and software is crucial for efficient data handling; for instance, operating systems manage memory allocation and deallocation, ensuring that data can be accessed and stored without performance bottlenecks[19].
Efficient Resource Management
The operating system plays a vital role in efficient resource management, ensuring that CPU, memory, and storage are utilized optimally[14]. It maintains records of which memory segments are in use and allocates resources accordingly, supporting a smooth user experience even when multiple applications are active[19]. Security software also interacts with hardware components to protect data and maintain network security, which has become increasingly important in the context of rising cybersecurity threats[21].
Impact on Society
The rise of smartphones has significantly transformed various aspects of society, reshaping how individuals communicate, work, and engage in daily activities. These devices have effectively merged communication and computing into one compact form, initially designed for business but now integral to personal and professional life[4][6].
Communication Transformation
Smartphones have altered traditional modes of interaction, facilitating instant mes- saging, voice calls, and video conferencing, thereby enabling connectivity that tran- scends geographical barriers. The advent of social media platforms, accessible via smartphones, has redefined community and relationship dynamics, creating new standards for connection and self-identity[5][6]. This transformation has contributed to an environment where communication norms and social etiquette are constantly evolving, often reflecting the dual nature of technological influence—both empower- ing and complicating interpersonal relationships[5].
Economic and Work Implications
The integration of smartphones into daily life has also impacted the workforce. The ability to work remotely has increased, especially during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to enhanced flexibility and a redefined organizational culture[24]- [6]. However, this shift has not come without challenges, as the boundaries between personal and professional lives become increasingly blurred.
Moreover, the economic landscape has adapted to mobile technology, with the rise of mobile e-commerce enhancing customer loyalty and retention[4]. Businesses have leveraged smartphones for marketing through targeted advertisements, often reducing overall marketing costs while increasing consumer engagement[4].
Social Dynamics and Challenges
While smartphones provide substantial benefits, they also pose significant chal- lenges to society. Issues such as digital addiction, social isolation, and reduced attention spans are becoming more prevalent as individuals increasingly rely on these devices for social interaction and information[4][5]. The potential for privacy violations and data vulnerabilities further complicates the societal impact of smart- phones, raising questions about security and ethical usage[4].
References
[1] : Smartphone History: A Detailed Timeline - CloudContactAI
[2] : Evolution of Mobile Phones: From Bricks to Smartphones
[3] : The Evolution of Smartphone Technology: A Thrilling Odyssey ... - Medium
[4] : Do Smartphones Have a CPU? (Here’s the Answer) - Hello Smart Life
[5] : An In-Depth Guide to CPU Performance in Smartphone Processors
[6] : What is an SoC? Everything you need to know about smartphone chipsets
[7] : How Do Smartphones Work? (A Comprehensive Guide)
[8] : How Software and Hardware Work Together? Interaction and ... - BlogMinutes
[9] : Mobile Hardware and Software:Key Parts,Components,Functions [10]: What is a Mobile Operating System? - GeeksforGeeks
[11] : What is a Mobile Operating System (Mobile OS ... - TechTarget
[12] : Mobile operating system - Wikipedia
[13] : Mobile Operating System: Definition,Types, Features and Examples - Toppr
[14] : How do Software and Hardware Work Together? – What to Know
[15] : Hardware and Software: How do they interact? - AMCEF
[16] : Cultural Differences in Telephone Use Around the World Insights and ...
[17] : How Mobile Phones Are Shaping Modern Social Norms A Deep Dive into ...
[18] : 9 greatest breakthroughs in cell phones - Android Authority
[19] : Smartphone Anatomy 101: Putting Your Phone Under The Microscope! [20]: How does your smartphone work? - Mobile phone technology explained
[21] : Impact of Smartphones on Society - Use of Mobile Phones
[22] : The Cultural Impact of Phone Communication How Mobile Phones Shape ...