How Does the Brain Work: A Simple Guide to Neuroscience
Discover how the human brain works in this comprehensive guide to neuroscience. Learn about brain structure, cognitive functions, neuroplasticity, and the best ways to maintain brain health.
Introduction
How Does the Brain Work: A Simple Guide to Neuroscience is an educational resource that demystifies the complexities of the human brain and its functions. As the central organ of the nervous system, the brain is responsible for processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and facilitating cognitive activities such as thinking, learning, and emotional regulation. Its intricate structure, composed of various specialized regions, allows it to perform a wide range of tasks, making it a focal point of interest in both scientific research and public understanding of neuroscience.
Notable for its exploration of cognitive functions, neuroplasticity, and brain health, this guide addresses the fundamental processes that govern how the brain operates. It examines key regions like the hippocampus, responsible for memory formation, and the prefrontal cortex, which plays a crucial role in decision-making and reasoning.
The guide also highlights the importance of maintaining brain health through lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management, which can significantly influence cognitive longevity and function.
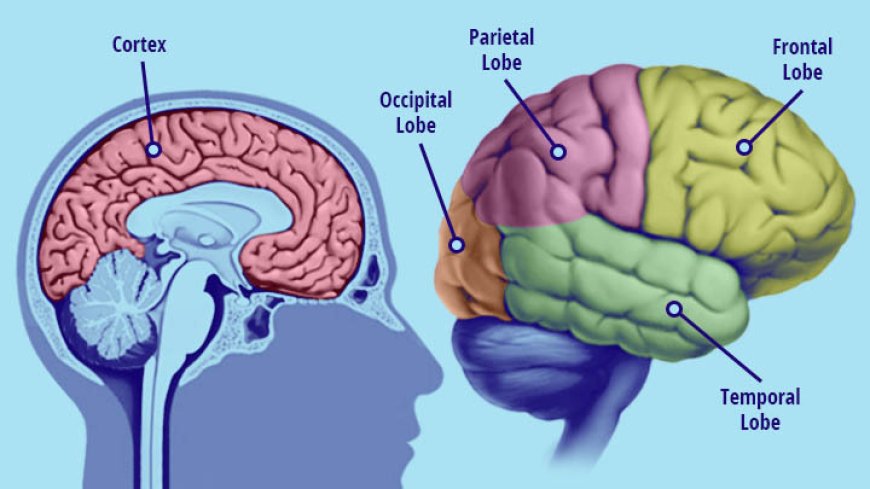
Photo showing the functions of different parts of the brain.
Controversies surrounding brain function often stem from ongoing debates in the field of neuroscience regarding the extent of localization versus network interactions within the brain. The historical shift from strict localizationist views to more integrated approaches illustrates the evolving understanding of brain functions and how multiple regions collaborate during cognitive tasks. The implications of neuroplasticity further complicate these discussions, particularly concerning recovery from injuries and the brain's ability to adapt in response to experience.
Overall, How Does the Brain Work serves as a foundational resource for individuals seeking to understand the brain's complexities, its role in shaping human behavior, and the latest advancements in neuroscience that continue to transform our comprehension of this vital organ.
Structure of the Brain
The human brain is an intricate organ central to the nervous system, primarily composed of soft nervous tissue and protected by the skull. It functions as the coordinating center for sensation, intellectual activity, and nervous processes, processing information received from the five senses: sight, smell, sound, touch, and taste, as well as inputs from internal organs and the environment.
Major Components of the Brain
The brain can be divided into three main parts:
-
Cerebrum – The largest component, overseeing cognitive functions such as thinking, memory, and decision-making.
-
Cerebellum – Crucial for coordination and movement.
-
Brainstem – Governs essential life-sustaining functions such as breathing and heart rate.
Brain Function
The brain is a highly organized and complex organ that serves as the epicenter of the central nervous system (CNS), responsible for processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and enabling cognitive activities such as thoughts, emotions, and memories. It interprets inputs from the five senses and integrates this information to give meaning to the surrounding world.
Communication and Processing
The brain processes and transmits information through a vast network of neurons. Neurons communicate via electrical signals known as action potentials, which allow rapid transmission of information across long distances within the nervous system. This communication is fundamental for various cognitive functions, including memory formation, attention, and decision-making.
Cognitive Functions
Cognitive functions encompass a range of mental processes that include:
-
Memory
-
Attention
-
Language
-
Problem-solving
-
Decision-making
Each of these processes relies on the coordinated efforts of different brain regions. For instance, the prefrontal cortex is heavily involved in reasoning and executive functions, while the hippocampus is essential for converting short-term memories into long-term storage.
Development and Learning
The brain exhibits remarkable plasticity, especially during critical developmental periods, which facilitates learning, including language acquisition. Neural networks are shaped by exposure to stimuli, allowing children to learn language more efficiently. Advancements in cognitive neuroscience continue to improve our understanding of these processes, leading to better treatments for cognitive disorders and enhanced insight into how we learn and remember.
Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, often referred to as brain plasticity, is the brain's remarkable ability to adapt and reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout an individual's life. This capacity allows the brain to modify its structure and function in response to various inputs, such as learning, experiences, and environmental changes.
Types of Neuroplasticity
Functional Plasticity
Functional plasticity pertains to the brain's ability to alter the functional properties of neural networks. This can occur through various mechanisms, including:
-
Homologous Area Adaptation – Cognitive processes transfer from a damaged brain region to its counterpart in the opposite hemisphere.
-
Map Expansion – Functions from one part of the brain are transferred to another region based on demand.
Structural Plasticity
Structural plasticity is the brain's ability to change its neuronal connections. This includes the ongoing production and integration of new neurons within the central nervous system throughout life. Structural neuroplasticity can be studied through various imaging methods, such as MRI and CT scans, which reveal alterations in brain anatomy, such as changes in grey matter or synaptic strength.
Role of Neuroplasticity in Recovery
Neuroplasticity plays a critical role in recovery from brain injuries, such as strokes or spinal cord injuries. Rehabilitation techniques that promote neuroplasticity, including physical therapy, cognitive exercises, and advanced technological interventions like brain-computer interfaces, have been shown to enhance recovery outcomes.
Brain Health
Maintaining brain health is crucial for overall well-being and cognitive functioning. The brain is a highly complex organ that is susceptible to a range of conditions and lifestyle factors that can affect its performance and longevity.
Factors Influencing Brain Health
Nutrition and Diet
A balanced diet rich in nutrients is essential for optimal brain function. Key nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants, support neurotransmitter synthesis and maintain the structural integrity of brain cells.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity enhances brain health by increasing blood flow and promoting neuroplasticity. Exercise is also associated with a lower risk of degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and other cognitive impairments.
Sleep
Sleep is vital for maintaining cognitive functions, including memory consolidation and emotional regulation. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to various psychiatric conditions, including anxiety and depression.
Protecting Brain Health
-
Stress Management – Chronic stress can negatively impact brain structure, particularly areas involved in memory, such as the hippocampus.
-
Mental Engagement – Learning new skills or engaging in social activities can protect against cognitive decline.
-
Neurotransmitter Balance – Imbalances in neurotransmitter systems can lead to cognitive impairments and conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and depression.
Historical Perspectives
Early Theories and Concepts
The understanding of brain function has evolved significantly over centuries. Early civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans, laid foundational ideas about the brain's role in cognition and behavior.
The 19th and Early 20th Centuries
The late 19th and early 20th centuries marked a pivotal era in brain research, with notable advances in understanding brain structures and their associated functions. Influential figures like Paul Broca and Carl Wernicke made significant discoveries regarding the localization of language functions in the brain.
Contemporary Developments
In recent years, advancements in technology and research methodologies have led to significant progress in understanding the brain's complexities. Modern neuroscience now incorporates various approaches, including cellular and molecular studies, systems neuroscience, and the development of brain mapping techniques.
References
[1] Brain: How It Works, Function, Parts & Conditions - Cleveland Clinic
[2] : Parts of the Brain and Their Functions - Science Notes and Projects
[3] : Cognitive Function Brain Areas: Mapping Mental Control
[4] : Anatomy of the Brain - AANS
[5] : Exploring the Impact of Neurotransmitter Diversity on Brain Function
[6] : Neural Pathways: Mechanisms, Influences, and Behavioral Impact
[7] : Cognitive Processes: Key Mechanisms of Information Processing in the ...
[8] : History of neuroscience - Wikipedia
[9] : Neuroplasticity - Wikipedia
[10] : Neuroplasticity After Brain Injury: Principles and Methods for ...
[11] : Importance of Neuroplasticity for Paralysis Recovery - Medicover Hospitals
[12] : A Renaissance brain - Mapping Ignorance
[13] : Parts of the Brain: Anatomy, Functions, and Conditions - Verywell Mind
[14] : The Role of Neurotransmitters in Brain and Cognitive Health
[15] : Function of Brain Regions: Key Areas and Their Roles in Cognitive ...
[16] : a history of explorations into brain function - SearchWorks catalog
[17] : The Cell Doctrine: A Historical View on Brain Function Theories
[18] : Brain Tracts: Essential Pathways for Neural Communication
[19] : History of Neuropsychology - BRAIN
[20] : 50 Years of Neuroscience: Progress and a Look Into the Future
[21] : How Do Different Brain Regions Interact to Enhance Function? Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works - Johns Hopkins Medicine