Africas Geographical Features Mountains, Deserts and Rivers
Discover Africa's diverse geographical features, from towering mountains like Kilimanjaro to vast deserts like the Sahara and mighty rivers like the Nile. Explore their impact on climate, culture, and wildlife.
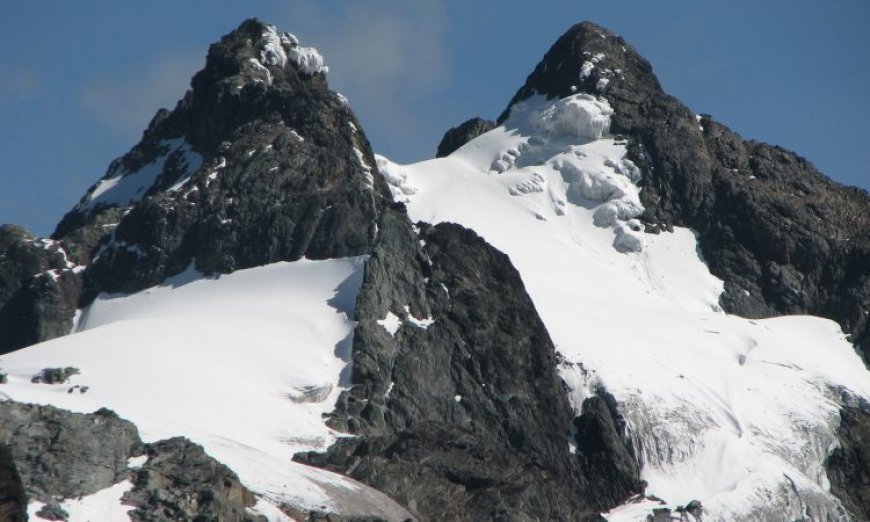

Africa's geographical features, including its mountains, deserts, and rivers, play a crucial role in shaping the continent's ecosystems, cultures, and economies. The continent is home to some of the world's most notable mountain ranges, such as the
These mountain systems not only attract adventure seekers but also serve as cultural landmarks for the indigenous communities residing in their shadow[1][2][3].
The deserts of Africa, most prominently the Sahara, represent the largest hot desert on Earth, encompassing over 9.2 million square kilometers and spanning multiple countries[4][5]. Despite their arid conditions, these deserts support a variety of flora and fauna adapted to extreme environments and house over 2 billion people who rely on these landscapes for their livelihoods. Moreover, the deserts are rich in mineral resources, contributing significantly to local and global economies. However, the challenges posed by climate change are threatening these delicate ecosystems and the communities that inhabit them, raising concerns about sustainability and resource management[6][7].
Africa's rivers, including the Nile, Congo, and Zambezi, are vital lifelines that nourish both the land and its people. The Nile, stretching over 4,000 miles, is not only the longest river in Africa but also central to the history and development of ancient civilizations, particularly in Egypt[8][9]. These rivers support agriculture, fishing, and transportation while providing essential water resources to millions. Nonetheless, increasing pressures from climate change and human activities jeopardize their health and the communities dependent on them[10][11].
Overall, Africa's mountains, deserts, and rivers are integral to the continent's identity and functionality. Their significance extends beyond mere geography; they are inter- twined with the cultural narratives, economic practices, and environmental challenges faced by the diverse populations inhabiting this rich and varied landscape.
Mountains
Africa is home to some of the most spectacular and unique mountain ranges in the world, each contributing to the continent's diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage. Among these, the Atlas Mountains, Drakensberg Mountains, Ethiopian Highlands, and Mount Kenya stand out for their geological significance and biodi- versity.
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains extend for over 1,200 miles across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, forming the geologic backbone of the Maghreb region. The highest peak, Mount Toubkal, rises to 13,671 feet and offers stunning panoramic views and chal- lenging treks for adventurers[1]. The region is inhabited primarily by the indigenous Berber people and boasts a rich variety of flora and fauna, including the Barbary macaque and Barbary leopard[12].
Drakensberg Mountains
Located in South Africa, the Drakensberg Mountains are known for their dramatic cliffs, rich biodiversity, and ancient rock art. This mountain range serves as a paradise for hikers and nature enthusiasts, providing a unique blend of cultural history and natural beauty[1].
Ethiopian Highlands
Referred to as the "Roof of Africa," the Ethiopian Highlands feature the highest peak in Ethiopia, Mount Ras Dashen, which reaches 14,928 feet[2]. This ancient mountain system is divided into distinct ecoregions, supporting diverse wildlife, including the endemic Walia ibex and Ethiopian wolf[12]. The region is also recognized for its unique plant life, characterized by montane forests and afro-alpine moorlands[12].
Mount Kenya
Situated in central Kenya, Mount Kenya is an extinct volcano that rises to 17,057 feet, making it the second-highest mountain in Africa[2]. Its summit, often capped with snow, presents a variety of climbing routes, attracting mountaineers from around the world. The diverse ecosystems found on its slopes include tropical forests and alpine meadows, showcasing a rich variety of plant and animal species[2].
Other Notable Mountains
In addition to these prominent ranges, Africa is dotted with other significant peaks, including Mount Meru in Tanzania and the Brandberg Massif in Namibia. Mount Meru, known for its challenging ascents, offers climbers an opportunity to experience its striking volcanic landscape[2]. Meanwhile, the Brandberg Massif is celebrated for its ancient rock art and unique desert ecology[1].
Deserts
Deserts are prominent geographical features in Africa, characterized by their extreme aridity, unique ecosystems, and significant cultural and economic importance. The most notable desert in Africa is the Sahara, the world's largest hot desert, spanning over 9.2 million square kilometers across several countries, including Algeria, Libya, and Egypt[3][4].
Ecological Diversity
Despite their harsh conditions, deserts support a wide variety of plant and an- imal species that have adapted to extreme environments. The Sahara features extensive sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and minimal vegetation, but it is home to uniquely adapted flora and fauna, such as acacia trees, date palms, and animals like dromedary camels and fennec foxes[3][5]. Other deserts in Africa, such as the
Namib Desert, are similarly rich in biodiversity, housing endemic species and diverse landscapes that attract researchers and tourists alike[13].
Human Inhabitance and Cultural Significance
Deserts are home to over 2 billion people globally, with many communities relying on their ecosystems for food security and livelihood. Desert populations have developed rich cultural traditions and handicrafts that contribute significantly to local economies and inter-cultural trade[6]. For instance, the indigenous pastoral groups living in the Namib Desert maintain a lifestyle that is intricately connected to the arid environment, showcasing the adaptability of human cultures in extreme conditions[13].
Economic Importance
The mineral wealth of deserts is another significant aspect, as they are often re- ferred to as "mineral wastelands" due to their rich deposits of valuable resources. Deserts contain essential minerals such as coal, copper, gold, iron ore, natural gas, and petroleum, which play a vital role in both local and global economies[6]. The extraction of these resources is crucial for various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and energy production.
Challenges and Climate Change
The arid environments of deserts face growing challenges from climate change, which can exacerbate water scarcity and threaten the delicate balance of these ecosystems. Changes in precipitation patterns and increased aridity pose risks not only to desert flora and fauna but also to the human communities that depend on these environments for survival[7]. As climate conditions evolve, understanding and conserving desert ecosystems becomes increasingly important for addressing envi- ronmental issues and ensuring the sustainability of the resources they provide[6][7].
Rivers
Africa is home to some of the longest and most significant rivers in the world, playing a crucial role in the continent's ecology, economy, and culture. The Nile River, stretching over 4,000 miles, is not only the longest river in Africa but also one of the most historically significant, particularly for the development of ancient
Egyptian civilization[8][14]. Its annual flooding enriched the surrounding soil, allowing for sustainable agriculture, which was fundamental to the civilization's growth[9].
Major Rivers
The Nile River
The Nile, often regarded as the lifeblood of Egypt, has served as a critical waterway for trade and transport, facilitating cultural exchange across regions[8][10]. It flows through eleven countries, including Uganda, Sudan, and Egypt, and is divided into two main tributaries: the White Nile and the Blue Nile[14].
The Congo River
As the second-longest river in Africa, the Congo River flows approximately 2,920 miles and is known for its depth, making it the deepest river in the world[10]. It originates in the highlands of northeastern Zambia and crosses the equator twice, discharging a vast volume of water into the Atlantic Ocean[10]. The river supports a diverse ecosystem and provides vital resources for over 75 million people living along its banks, facilitating trade and transport of goods such as timber and miner- als[10][15].
The Zambezi River
The Zambezi River is Africa's fourth-longest river at about 1,599 miles. It flows east- ward through several countries, including Zambia, Angola, Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe, before discharging into the Indian Ocean[15][9]. The river is renowned for its scenic beauty, particularly at Victoria Falls, and serves as an important resource for agriculture and hydroelectric power for millions of people[15][9].
Other Notable Rivers
Other significant rivers in Africa include the Niger River, which provides crucial irrigation and trade routes in West Africa, and the Shebelle River, which plays a vital role in the arid regions of Somalia[16][15]. The Orange River serves as a natural border between South Africa and Namibia, while the Zambezi's basin supports a diverse array of wildlife and human communities[17][9].
Environmental and Economic Importance
The rivers of Africa are essential for sustaining local populations and ecosystems. They provide water for drinking, agriculture, and industry, and many are vital for fish- ing and transportation[10][17]. However, climate change poses significant challenges to these waterways, impacting water levels and the livelihoods of those who depend on them, as seen with the drying up of the Nile[11][15].
FAQs
1. What is the desert landform in Africa?
A desert landform in Africa refers to a vast, arid region with little rainfall, sparse vegetation, and extreme temperature variations. These landforms include sand dunes, rocky plateaus, dry riverbeds (wadis), and salt flats.
Example from East Africa:
- The Chalbi Desert in Kenya is a desert landform characterized by sandy and rocky terrain with occasional salt pans.
2. What type of mountains are found in Africa?
Africa has different types of mountains, including:
- Volcanic Mountains (formed by volcanic activity) – e.g., Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania).
- Fold Mountains (formed by the folding of the Earth's crust) – e.g., the Atlas Mountains in North Africa.
- Block Mountains (formed by faulting) – e.g., the Rwenzori Mountains (Uganda & DRC).
3. What are the three deserts in Africa?
The three major deserts in Africa are:
- Sahara Desert – The largest hot desert, covering North Africa.
- Kalahari Desert – Found in Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa.
- Namib Desert – A coastal desert along Namibia and Angola.
4. Where is the mountain in Africa?
Mountains in Africa are found in various regions:
- East Africa – Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania), Mount Kenya (Kenya), Rwenzori Mountains (Uganda).
- North Africa – The Atlas Mountains (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia).
- Central Africa – Mount Cameroon (Cameroon).
5. How many deserts are there in Africa?
Africa has at least 10 major deserts, including the Sahara, Kalahari, Namib, Danakil, Chalbi, Karoo, and Libyan Desert.
6. What is an example of a desert landform?
A sand dune is a common desert landform formed by wind deposition of sand.
Example in East Africa:
- The Erg Chebbi Dunes in Sudan.
7. What are examples of landforms?
Common landforms include:
- Mountains (e.g., Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania)
- Plateaus (e.g., Ethiopian Highlands)
- Valleys (e.g., Great Rift Valley)
- Deserts (e.g., Chalbi Desert, Kenya)
- Rivers (e.g., Nile River)
8. What is the largest desert in Africa?
The Sahara Desert, covering about 9.2 million km², is the largest desert in Africa and the third largest in the world.
9. What are the landforms of the Sahara Desert?
The Sahara Desert has diverse landforms, including:
- Ergs (large sand dunes)
- Regs (rocky deserts)
- Hamada (barren plateaus)
- Oases (fertile areas with water sources)
10. What are the characteristics of deserts in Africa?
- Low rainfall (less than 250 mm annually)
- Extreme temperatures (hot days, cold nights)
- Sparse vegetation (mostly drought-resistant plants)
- Wind erosion (shaping dunes and rock formations)
- Presence of oases (water sources in some areas)
11. What is the largest landform in Africa?
The Sahara Desert is the largest landform in Africa.
12. What type of land is a desert?
A desert is a dry, arid land with little to no rainfall, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
13. What are the top 5 highest mountains in Africa?
- Mount Kilimanjaro – 5,895 m (Tanzania)
- Mount Kenya – 5,199 m (Kenya)
- Mount Stanley (Rwenzori) – 5,109 m (Uganda/DRC)
- Mount Speke – 4,890 m (Uganda)
- Mount Baker – 4,844 m (Uganda)
14. What is the largest mountain in the world?
The largest mountain in the world by height is Mount Everest (8,848.86 m) in the Himalayas, Nepal.
15. Which desert is found in the northern part of Africa?
The Sahara Desert dominates North Africa, covering countries like Egypt, Libya, Algeria, and Sudan.
16. What is the 3rd largest mountain in Africa?
Mount Stanley (Rwenzori Mountains) – 5,109 m (Uganda & DRC).
17. What are the five major mountains in East Africa?
- Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania) – 5,895 m
- Mount Kenya (Kenya) – 5,199 m
- Mount Stanley (Rwenzori Mountains) (Uganda/DRC) – 5,109 m
- Mount Elgon (Uganda/Kenya) – 4,321 m
- Mount Meru (Tanzania) – 4,562 m
References
[1] : 15 Highest Mountains In Africa You Need To Visit In 2024
[2] : 10 Major Mountain Ranges of Africa - WorldAtlas
[3] : Top 10 Highest Mountains in Africa — The Ultimate Guide - Altezza Travel
[4] : Preserving the Sahara: Conservation Efforts in the Desert
[5] : Sahara - Wikipedia
[6] : Sahara Desert - WorldAtlas
[7] : The Deserts Of Africa - WorldAtlas
[8] : 15 Reasons Why Deserts Are Important - Curious Desire
[9] : Cross-Chapter Paper 3: Deserts, Semiarid Areas and Desertification - IPCC
[10] : Exploring the Fascinating History and Culture Along the Nile River
[11] : The Nile River: Unveiling Its Historic And Cultural Significance
[12] : Flowing Through History: The Nile’s Impact on Egypt - AKEM
[13] : 10 Longest Rivers In Africa - WorldAtlas
[14] : 10 Major Rivers in Africa and their Location - Within Nigeria
[15] : The 18 Most Famous Rivers of Africa - The geography teacher
[16] : Rethinking the Politics of Transboundary Water Management ... - UNU-CRIS
: What are the 4 rivers in Africa? - Geographic FAQ Hub: Answers ... - NCES