How Marine Pollution Affects Ocean Life: A Scientific Study
Marine pollution, which includes waste such as plastics and harmful chemicals, has a devastating effect on ocean life. It leads to animals getting entangled, ingesting debris, the destruction of habitats, and the spread of toxic substances through the food chain—putting biodiversity and the overall health of marine ecosystems at serious risk.

Marine pollution is one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. It poses significant threats to the health of ocean ecosystems, endangering marine species and, by extension, the global environment. This article explores the effects of marine pollution on ocean life, drawing from scientific studies to highlight the severity of the problem and the necessary actions required to mitigate its impacts.
What is Marine Pollution?
Marine pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or pollutants into the ocean, leading to a degradation of marine ecosystems. These pollutants can originate from a wide variety of sources, including land-based activities, maritime industries, and natural occurrences. Marine pollution encompasses various types of pollutants, such as chemicals, plastics, heavy metals, and even noise.
Reseach Data by Hull showing the effects of water pollution.
Types of Marine Pollution
Marine pollution is not limited to one form. In fact, it takes on many different faces, and its effects can be seen across various types of pollutants:
Chemical Pollution
Chemical pollutants, such as oil spills, pesticides, and heavy metals, are one of the primary causes of marine pollution. These toxins can have deadly effects on marine life by poisoning fish, corals, and other organisms. Chemicals can also disrupt reproductive processes, leading to population declines.
Plastic Pollution
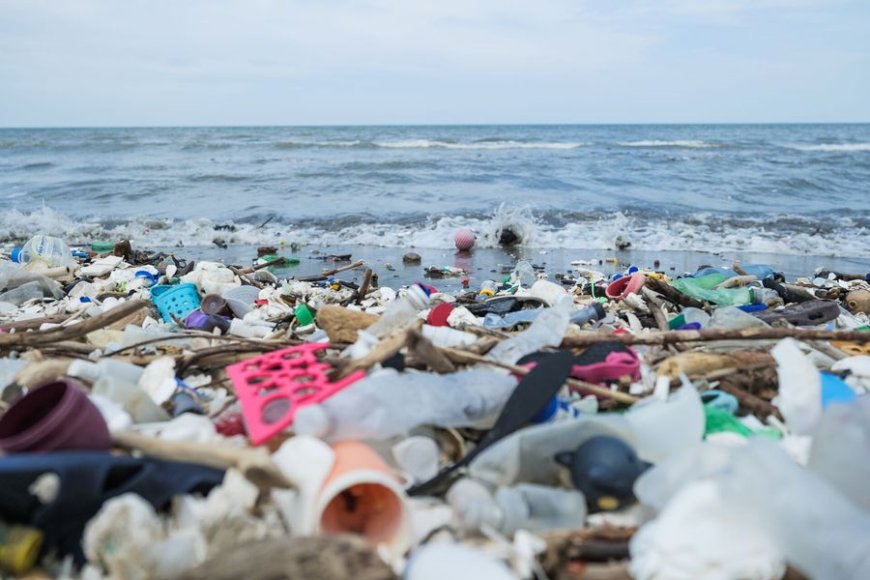
Plastic pollution is one of the most pervasive forms of marine pollution. Discarded plastic items such as bottles, bags, and microplastics often end up in the oceans. These plastics can harm marine animals that ingest or become entangled in them, leading to injury, malnutrition, or death.
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution, although less visible, is just as harmful. It affects marine species, particularly whales, dolphins, and other aquatic mammals, whose communication relies heavily on sound. Increased human activity in the oceans, such as shipping and oil exploration, generates underwater noise that interferes with these animals' natural behaviors, including mating, hunting, and navigation.
Main Sources of Marine Pollution
Marine pollution is primarily caused by human activities. These activities often occur on land but have far-reaching consequences for the oceans. Below are the main sources of marine pollution:
Industrial Waste
Industries, particularly those located near coastal regions, are significant contributors to marine pollution. Chemicals and waste products are often released directly into the ocean, either accidentally or as part of regular operations. Industrial runoff can contain a range of harmful substances that are toxic to marine life.
Agricultural Runoff
The use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture leads to the runoff of harmful chemicals into nearby rivers and eventually into the ocean. These chemicals can cause algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and a reduction in biodiversity in marine environments.
Urban and Coastal Development
Rapid urbanization and coastal development contribute to pollution by increasing the amount of waste and chemicals that enter the oceans. Construction debris, sewage, and untreated waste can pollute coastal ecosystems, affecting marine life in the process.
Scientific Studies on Marine Pollution
Scientific studies have played a crucial role in understanding the effects of marine pollution on ocean life. Research has shown the far-reaching consequences of pollution, not only on marine species but also on the broader ecosystem.
Ocean pollution with plastics
Effects on Marine Species
Marine pollution has devastating effects on marine species, both at the individual level and within populations. Pollution can cause disease, disrupt reproduction, and lead to population declines. It also has indirect effects, such as food scarcity and habitat destruction.
Coral Reefs and Marine Flora
Coral reefs, often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," are especially vulnerable to pollution. Chemical pollutants, excess nutrients from agricultural runoff, and plastic debris can harm coral reefs, leading to coral bleaching and reduced biodiversity.
Marine Fauna (Fish, Mammals, etc.)
Pollutants such as plastics, chemicals, and oil spills are dangerous to marine animals, from small fish to large mammals like whales and dolphins. Ingesting or becoming entangled in plastic can result in suffocation or starvation. Similarly, oil spills can coat marine animals' fur or feathers, affecting their ability to regulate body temperature.
Long-Term Environmental Impact
Marine pollution has long-term consequences that disrupt the entire marine ecosystem. It alters the composition of species, damages habitats, and even affects the global climate system.
Disruption of Food Chains
Pollution affects the marine food chain, which relies on a delicate balance of species. When pollutants enter the food chain, they can cause the decline of important species and disrupt predator-prey relationships. This can lead to an overall decrease in marine biodiversity.
Climate Change and Ocean Health
The pollution of oceans also contributes to climate change. For example, excess nutrients from agricultural runoff can lead to algal blooms that deplete oxygen in the water, creating "dead zones" where marine life cannot survive. Additionally, the destruction of coastal ecosystems like mangroves and seagrass beds, which act as carbon sinks, further accelerates climate change.
Efforts to Combat Marine Pollution
To combat marine pollution, various global initiatives and policies have been put in place to reduce pollution and protect marine ecosystems.
International Agreements and Policies
Governments around the world have enacted international agreements aimed at reducing marine pollution. These include conventions such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which seeks to regulate and manage pollution and protect marine biodiversity.
The Role of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) play a key role in safeguarding marine life. These areas are designated regions where human activities are restricted or controlled to help preserve marine ecosystems. MPAs contribute to reducing the effects of pollution, allowing marine life to recover.
Technological Innovations for Pollution Reduction
Advances in technology are helping to address marine pollution. From floating waste collection devices to biodegradable materials, new innovations are being used to reduce the amount of waste entering the oceans. Additionally, researchers are developing more effective methods for cleaning up oil spills and plastics.
How Individuals Can Help Reduce Marine Pollution
While large-scale initiatives are crucial, individuals also play a significant role in reducing marine pollution. Here are some ways to make a positive impact:
Reducing Plastic Waste
One of the most important steps individuals can take is to reduce plastic waste. This includes using reusable bags, bottles, and containers, as well as avoiding single-use plastics.
Supporting Marine Conservation Initiatives
Individuals can support marine conservation efforts by donating to or volunteering with organizations that focus on ocean health, such as the Ocean Conservancy or the Marine Conservation Society.
Participating in Beach Clean-Ups
Beach clean-up events are an effective way to remove plastic and other pollutants from the ocean. By participating in or organizing clean-up efforts, individuals can help remove waste before it has a chance to harm marine life.
Key Facts About Marine Pollution
|
Fact |
Details |
|
Plastic Waste |
Over 8 million metric tons of plastic enter the oceans each year, affecting marine life. |
|
Chemical Pollutants |
Chemicals like oil and pesticides contribute to the poisoning of marine species and ecosystems. |
|
Dead Zones |
Over 400 "dead zones" exist in oceans globally, where oxygen depletion from pollution kills marine life. |
|
Impact on Coral Reefs |
Coral reefs are highly sensitive to pollution, with increased pollutants causing coral bleaching and die-offs. |
|
Marine Species Affected |
Over 700 marine species are affected by pollution, including whales, dolphins, and sea turtles. |
|
Global Efforts |
Initiatives like the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea aim to reduce marine pollution worldwide. |
|
Plastic Breakdown |
It can take over 400 years for plastic to break down in the ocean, continuing to harm wildlife. |
|
Algal Blooms |
Excess nutrients from pollution can trigger harmful algal blooms that deplete oxygen and suffocate marine life. |
|
Oil Spills |
Oil spills can have long-lasting effects on marine ecosystems, with some spills taking decades to recover. |
|
Noise Pollution |
Increased noise from shipping and industrial activities disrupts marine mammals' communication. |
|
Agricultural Runoff |
Runoff from farms carries fertilizers and pesticides into oceans, contributing to nutrient pollution. |
|
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) |
MPAs are essential for preserving biodiversity, providing safe zones where pollution is controlled. |
|
Technology Innovations |
New technologies are being developed to clean oceans, including drones, barriers, and waste-collecting devices. |
|
Impact on Human Health |
Polluted oceans impact human health by contaminating seafood, leading to potential toxins entering human diets. |
|
Global Solutions |
Worldwide efforts, including policy changes and cleaner technologies, are being implemented to tackle marine pollution. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does marine pollution affect the food chain?
Marine pollution disrupts the food chain by contaminating water sources, harming smaller species that are consumed by larger predators, and ultimately affecting the entire ecosystem's balance.
What are the most common pollutants in the ocean?
The most common ocean pollutants include plastics, chemicals (such as pesticides and heavy metals), oil, and noise.
Can marine pollution be completely eliminated?
While eliminating marine pollution entirely is challenging, efforts to reduce pollution and increase awareness can significantly mitigate its impact on ocean life.
How does marine pollution affect humans?
Marine pollution affects humans by damaging ecosystems that we rely on for food and resources, as well as contributing to climate change, which has global consequences for human populations.
What are the effects of oil spills on marine life?
Oil spills coat marine organisms' bodies, disrupting their ability to regulate temperature and breathe. They can also cause long-term ecological damage by contaminating habitats.
What can I do to reduce my contribution to marine pollution?
You can reduce your contribution by minimizing plastic use, properly disposing of waste, supporting conservation efforts, and raising awareness about the importance of protecting our oceans.
Conclusion
Marine pollution poses a serious threat to ocean life and, by extension, to human well-being. Understanding the causes and consequences of pollution, along with taking collective action, is essential for safeguarding our oceans and their biodiversity. By supporting policies, reducing waste, and promoting conservation efforts, we can help protect marine life for generations to come.