Africa's Equatorial Climate: Year-Round Warmth
Discover the unique features of Africa's equatorial climate, where year-round warmth, high humidity, and abundant rainfall shape the region's environment, wildlife, and way of life.
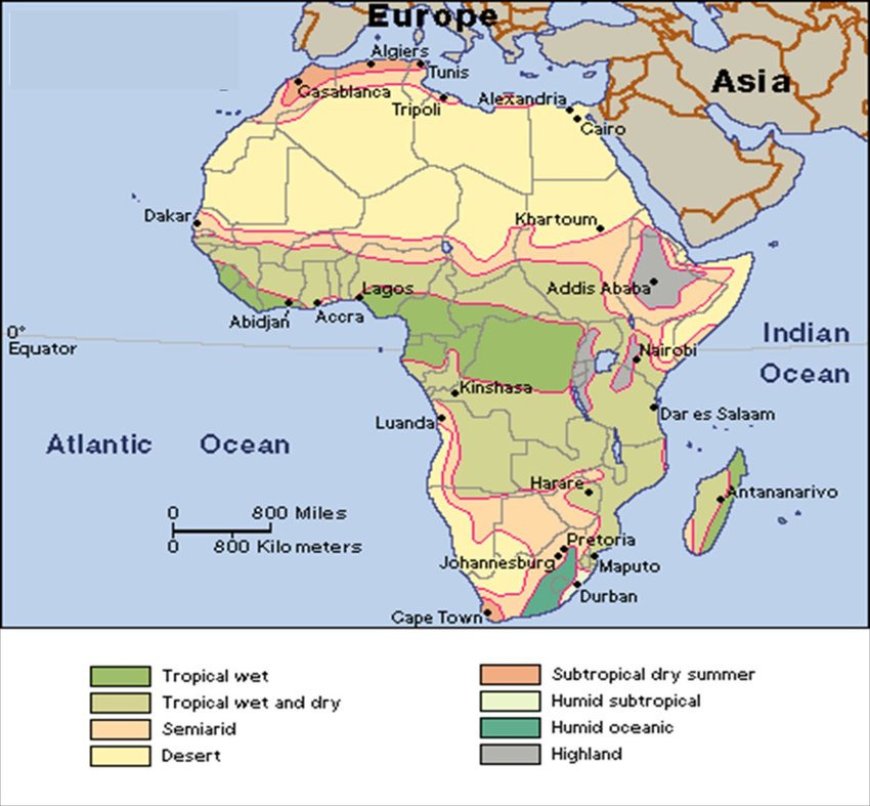
Introduction
Imagine a place where the sun seems to shine brighter, the air fills with the lively chatter of diverse wildlife, and the lush greenery never fades away. Welcome to Africa's equatorial region—a unique climate zone that boasts warmth and vibrancy throughout the year. In this article, we will explore the defining characteristics of Africa's equatorial climate, its impact on biodiversity, human life, and its unique seasons. Get ready to embark on a journey into one of the planet's most intriguing climates.
Understanding Equatorial Climate
Africa's equatorial climate is primarily found around the equator, spanning several countries, including the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Cameroon, and parts of Uganda and Kenya.
Characteristics of Equatorial Climate
- Temperature: One of the most striking features of this climate is the consistently high temperatures, often averaging between 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F) year-round. Even at night, temperatures rarely drop significantly.
- Humidity: The region experiences high humidity levels, often exceeding 85%. This moisture in the air not only contributes to discomfort but also fosters rich ecosystems.
- Rainfall: Equatorial Africa is known for its substantial rainfall, receiving between 1750 mm to 2500 mm (approximately 69 to 98 inches) annually. Rainfall is typically distributed throughout the year, with slight variations in wet and dry seasons.
Did You Know? The heavy rainfall is essential for maintaining the extensive tropical rainforests that characterize much of the equatorial region.
The Impact of Equatorial Climate on Biodiversity
The warm temperatures and ample rainfall make Africa's equatorial climate a hotspot for biodiversity.
Flora and Fauna
- Rainforests: The Congo Basin, often referred to as the "lungs of Africa," is home to some of the world's largest tropical rainforests. These forests are rich in species diversity, hosting more than 10,000 species of plants, including many that are endemic.
- Wildlife: The lush landscapes provide habitats for an astonishing array of wildlife. Common residents include:
- Gorillas and chimpanzees
- Elephants
- An array of colorful birds like the African Grey Parrot
- Frogs and reptiles that thrive in humid conditions
Conservation Efforts
Maintaining such biodiversity is crucial, leading to targeted conservation efforts. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) work tirelessly to protect endangered species and restore habitats. You can learn more about their initiatives on their official website.
Human Life in Equatorial Africa
The distinct climate not only shapes the environment but also influences the lives of the people who inhabit these regions.
Livelihoods
- Agricultural Practices: The fertile lands nurtured by regular rainfall allow for agriculture to flourish. Common crops include cassava, yams, and banana, which are staple foods for many communities.
- Cultural Richness: The diverse cultures in this region are closely tied to the climate. Traditional practices often incorporate the natural resources available, with many societies relying on the forest for food, shelter, and medicine.
Quote: "The richness of culture in equatorial Africa is as vibrant as the landscapes themselves. It's a symbiotic relationship between nature and human life."
Unique Seasons in Equatorial Africa
While one might think that all equatorial regions experience the same weather year-round, there are distinct wet and dry seasons that vary slightly across the region.
Wet and Dry Seasons
- Long Wet Season: Typically occurring from March to May, this period sees the heaviest rainfall, fostering extensive plant growth. Rivers swell, and wildlife flourishes.
- Short Dry Season: In June and July, lighter rains may still occur, but conditions begin to dry out, allowing for easier travel and agricultural activities.
- Second Wet Season: From August to October, another surge of rainfall enhances biodiversity further, with fruit trees bearing abundant crops.
- Short Dry Season: November and December provide a brief respite before heavy rains return, leading to a cycle of regeneration.
Climate Change Considerations
The impact of climate change poses a significant threat to these delicate ecosystems. As global temperatures rise and rainfall patterns shift, the resilience of the flora and fauna in equatorial Africa could decline. Efforts to combat climate change through sustainable practices are critical for the future.
Conclusion
Africa's equatorial climate is a remarkable phenomenon characterized by year-round warmth, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. This climate not only supports a rich tapestry of biodiversity but also shapes the lives of millions who inhabit the region. Understanding this unique environment is crucial, as it highlights the intricate balance between nature and human life.
As we move forward, let's appreciate the beauty and complexity of equatorial Africa and commit to preserving its invaluable resources for generations to come. So next time you imagine Africa, think of its warm embrace and vibrant ecosystems that thrive under the equatorial sun.
Call to Action
Have you visited Africa's equatorial region? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below! Let’s discuss ways we can all contribute to the protection of these incredible ecosystems.
References:
- World Wildlife Fund
- National Geographic articles on Africa's ecosystems.
Introduction
Imagine a place where the sun seems to shine brighter, the air fills with the lively chatter of diverse wildlife, and the lush greenery never fades away. Welcome to Africa's equatorial region—a unique climate zone that boasts warmth and vibrancy throughout the year. In this article, we will explore the defining characteristics of Africa's equatorial climate, its impact on biodiversity, human life, and its unique seasons. Get ready to embark on a journey into one of the planet's most intriguing climates.
Understanding Equatorial Climate
Africa's equatorial climate is primarily found around the equator, spanning several countries, including the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Cameroon, and parts of Uganda and Kenya.
Characteristics of Equatorial Climate
- Temperature: One of the most striking features of this climate is the consistently high temperatures, often averaging between 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F) year-round. Even at night, temperatures rarely drop significantly.
- Humidity: The region experiences high humidity levels, often exceeding 85%. This moisture in the air not only contributes to discomfort but also fosters rich ecosystems.
- Rainfall: Equatorial Africa is known for its substantial rainfall, receiving between 1750 mm to 2500 mm (approximately 69 to 98 inches) annually. Rainfall is typically distributed throughout the year, with slight variations in wet and dry seasons.
Did You Know? The heavy rainfall is essential for maintaining the extensive tropical rainforests that characterize much of the equatorial region.
The Impact of Equatorial Climate on Biodiversity
The warm temperatures and ample rainfall make Africa's equatorial climate a hotspot for biodiversity.
Flora and Fauna
- Rainforests: The Congo Basin, often referred to as the "lungs of Africa," is home to some of the world's largest tropical rainforests. These forests are rich in species diversity, hosting more than 10,000 species of plants, including many that are endemic.
- Wildlife: The lush landscapes provide habitats for an astonishing array of wildlife. Common residents include:
- Gorillas and chimpanzees
- Elephants
- An array of colorful birds like the African Grey Parrot
- Frogs and reptiles that thrive in humid conditions
Conservation Efforts
Maintaining such biodiversity is crucial, leading to targeted conservation efforts. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) work tirelessly to protect endangered species and restore habitats. You can learn more about their initiatives on their official website.
Human Life in Equatorial Africa
The distinct climate not only shapes the environment but also influences the lives of the people who inhabit these regions.
Livelihoods
- Agricultural Practices: The fertile lands nurtured by regular rainfall allow for agriculture to flourish. Common crops include cassava, yams, and banana, which are staple foods for many communities.
- Cultural Richness: The diverse cultures in this region are closely tied to the climate. Traditional practices often incorporate the natural resources available, with many societies relying on the forest for food, shelter, and medicine.
Quote: "The richness of culture in equatorial Africa is as vibrant as the landscapes themselves. It's a symbiotic relationship between nature and human life."
Unique Seasons in Equatorial Africa
While one might think that all equatorial regions experience the same weather year-round, there are distinct wet and dry seasons that vary slightly across the region.
Wet and Dry Seasons
- Long Wet Season: Typically occurring from March to May, this period sees the heaviest rainfall, fostering extensive plant growth. Rivers swell, and wildlife flourishes.
- Short Dry Season: In June and July, lighter rains may still occur, but conditions begin to dry out, allowing for easier travel and agricultural activities.
- Second Wet Season: From August to October, another surge of rainfall enhances biodiversity further, with fruit trees bearing abundant crops.
- Short Dry Season: November and December provide a brief respite before heavy rains return, leading to a cycle of regeneration.
Climate Change Considerations
The impact of climate change poses a significant threat to these delicate ecosystems. As global temperatures rise and rainfall patterns shift, the resilience of the flora and fauna in equatorial Africa could decline. Efforts to combat climate change through sustainable practices are critical for the future.
Conclusion
Africa's equatorial climate is a remarkable phenomenon characterized by year-round warmth, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. This climate not only supports a rich tapestry of biodiversity but also shapes the lives of millions who inhabit the region. Understanding this unique environment is crucial, as it highlights the intricate balance between nature and human life.
As we move forward, let's appreciate the beauty and complexity of equatorial Africa and commit to preserving its invaluable resources for generations to come. So next time you imagine Africa, think of its warm embrace and vibrant ecosystems that thrive under the equatorial sun.
Call to Action
Have you visited Africa's equatorial region? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below! Let’s discuss ways we can all contribute to the protection of these incredible ecosystems.
References:
- World Wildlife Fund
- National Geographic articles on Africa's ecosystems.