Desertification in Africa: Exploring Challenges and Unveiling Effective Solutions
Desertification in Africa threatens livelihoods, agriculture, and ecosystems. Explore its causes, impacts, and effective solutions to combat land degradation and restore sustainability across the continent.
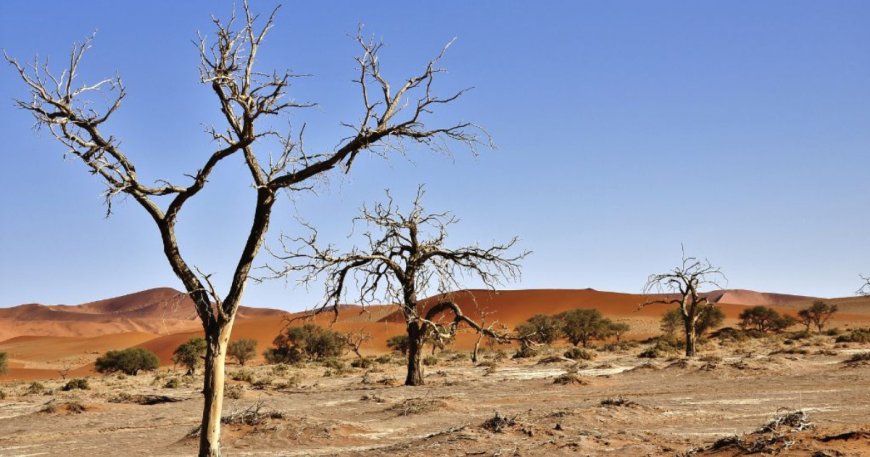

Desertification stands as one of the most pressing environmental issues facing Africa today. It refers to the degradation of land in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas, primarily due to human activities and climatic variations. This process significantly affects biodiversity, soil fertility, and water resources, ultimately jeopardizing the livelihoods of millions across the continent.
Understanding the root causes of desertification is crucial to addressing its challenges. Factors contributing to this phenomenon include overgrazing, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices, which strip the soil of its nutrients and expose it to erosion. Additionally, climate change exacerbates these effects, leading to increased temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns.
“Desertification is not just an environmental issue; it’s a social and economic issue that requires urgent and coordinated action,” says Dr. Amadou Ba, a leading environmental scientist.
As someone interested in the future of our planet, realizing the severe impacts of desertification becomes an imperative first step. For the communities living on the frontlines, these impacts can be particularly devastating. The loss of arable land often results in food insecurity and increased poverty levels, prompting migration and conflict over dwindling resources.
To tackle desertification, concerted efforts from governments, NGOs, and local communities are needed. These efforts can encompass:
• Implementing sustainable land management practices
• Restoring degraded lands through reforestation and agroforestry
• Raising awareness and building resilience against climate change impacts
By understanding desertification and embracing sustainable solutions, we can protect Africa’s landscapes and secure a prosperous future for its people. Desertification occurs when fertile land becomes progressively dry and barren, often resulting from unsustainable agricultural practices, deforestation, and climate change. But why is this a pressing issue? Desertification directly affects the livelihoods of millions in Africa, where about two-thirds of the continent is desert or dryland.
The impacts are multifaceted: it reduces agricultural productivity, leads to food insecurity, and worsens poverty levels. Furthermore, it causes biodiversity loss as vital habitats diminish due to the expansion of arid areas. With approximately 60% of Africa's population dependent on agriculture for their livelihoods, tackling this environmental challenge is essential.
Solutions to Desertification in Africa
However, there is hope and opportunity. Solutions lie in sustainable land management practices, innovative agricultural techniques, and policy reforms. For example:
• Agroforestry: Integrating trees into farming systems can enhance soil fertility, reduce erosion, and provide additional sources of income through fruit and wood production.
• Water Harvesting: Techniques such as rainwater collection and the construction of small dams can improve water availability for crops and livestock.
• Community Engagement: Grassroots involvement ensures the active participation of local communities in decision-making processes, fostering a sense of ownership over projects aimed at combating desertification.
By acting cohesively, we can mitigate the effects of desertification and safeguard the environment while fostering economic growth. Together, these efforts illuminate a path toward a more sustainable and prosperous continent. Acting unified also entails addressing root causes, such as unsustainable land use practices and overgrazing. By prioritizing holistic practices, we can implement sustainable farming techniques that increase productivity without depleting vital resources. Moreover, embracing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind can reduce our carbon footprint.
Map of Africa showing Desertification coverage
Supporting grassroots movements and engaging local communities are equally vital. When individuals are empowered with knowledge and resources, they become proactive stewards of their land. This is where initiatives like the Action Against Desertification and Africa's Great Green Wall play pivotal roles. By investing in large-scale reforestation and agroforestry projects, they aim to restore vast swathes of degraded land, benefitting both the environment and local economies.
International cooperation cannot be overlooked either. Treaties and agreements facilitated by organizations like the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) gather resources and expertise from around the globe, fostering a collaborative effort to tackle this pressing issue. By working together, we not only combat desertification but also progress towards achieving sustainable development goals.
Engaging in these solutions individually and collectively, we can not only combat desertification effectively but also nurture a resilient, thriving African ecosystem. Let's embark on this journey together for a brighter, greener future. To provide a clearer understanding of the impact and progress of combating desertification, here's a table showcasing key efforts and results in selected regions across Africa:
|
Region |
Initiative |
Land Restored (hectares) |
Communities Benefited |
|
North Africa |
Great Green Wall |
10,000,000 |
500,000 |
|
Sahel |
Pan-African Agenda on Ecosystem Restoration |
5,000,000 |
350,000 |
|
Southern Africa |
Action Against Desertification |
3,000,000 |
200,000 |
ertification affects approximately 45% of Africa's land area.These stark numbers bring to light a pressing environmental issue, but understanding the profound impacts and viable solutions is crucial. First, let's explore how desertification affects not only the land but also the people and ecosystems that depend on it.
The Broad Impacts of Desertification
Desertification is not just about barren landscapes. It leads to loss of biodiversity, affecting both flora and fauna unique to Africa's ecosystems. This disruption threatens food security when agricultural lands become less productive.
Socioeconomic Challenges
For many Africans, especially those living in rural areas, the quality of land directly impacts their livelihood. A degraded land means less nutritious crops, leading to food shortages and economic hardship.
With 60% of the African population living in susceptible areas, the economic consequences are significant. Consider that soil depletion costs Africa approximately 3% of its GDP annually. This financial strain stunts development in vulnerable communities.
The Climate Factor
As the globe warms, climate-induced desertification further complicates these challenges. Africa, despite its low carbon footprint, bears a hefty cost of rising temperatures that exacerbate desertification.
Pathways to Solutions
However, it's not all bleak. Solutions are within reach. Sustainable land management practices have been effective in reclaiming land. Take Ethiopia, for instance, where extensive efforts have restored millions of hectares.
Community Involvement and Innovation
Engaging local communities in land management ensures sustainable practices. Combined with innovative technologies and policies, these efforts pave the way for a more resilient future.
The key takeaway? While daunting, the challenge of desertification in Africa is met with ambition and actionable solutions, fostering hope for the continent's vibrant landscapes and the people who call it home. Desertification in Africa has become a pressing issue, impacting vast swathes of land and its inhabitants. The phenomenon, once a slow-moving calamity, is now accelerating thanks to factors like excessive agricultural practices, deforestation, and climate change. These elements escalate the transformation of fertile soil into arid ground, severely affecting both local communities and wildlife. Yet, understanding these challenges is the first step to paving a path towards sustainable solutions.
Desertification doesn't merely reshape the landscape; it alters the very fabric of African societies, economies, and ecosystems. With over 65% of Africa's productive land now degraded, the cascading effects are profound. Beyond the obvious environmental impacts, it disrupts daily lives, threatens food security, and fuels conflicts over diminishing resources.
However, hope is not lost. With concerted efforts towards sustainable land management, innovation, and a focus on community-led approaches, there are opportunities to counteract the tide of desertification. The journey might be long, but the collective power of informed action and technological advancement provides a promising o
FAQs:
1. What is desertification, and why is it a concern in Africa?
Desertification is the process of land degradation in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas due to factors like climate change and human activities. In Africa, it threatens food security, water availability, and biodiversity.
2. What are the main causes of desertification in Africa?
Key causes include deforestation, overgrazing, unsustainable farming practices, climate change, and prolonged droughts, all of which contribute to soil erosion and loss of vegetation cover.
3. How does desertification impact local communities?
It leads to reduced agricultural productivity, water scarcity, food insecurity, displacement of communities, and economic losses, especially in regions heavily reliant on farming and livestock.
4. What regions in Africa are most affected by desertification?
The Sahel region, parts of North Africa, East Africa, and the Horn of Africa are among the most affected due to extreme drought conditions and land degradation.
5. What are some effective solutions to combat desertification?
Solutions include afforestation and reforestation, sustainable farming practices, water conservation techniques, soil restoration methods, and policies promoting land rehabilitation and climate adaptation.
6. What is the Great Green Wall initiative?
The Great Green Wall is an African-led initiative aiming to restore degraded land across the Sahel region by planting trees and promoting sustainable land management to combat desertification and improve livelihoods.
7. How can individuals contribute to fighting desertification?
People can help by planting trees, adopting sustainable farming and water conservation methods, supporting policies that protect land resources, and raising awareness about desertification’s impacts and solutions.