What Sets the Caucasus Mountains Apart from the Ural Mountains?
Discover the key differences between the Caucasus and Ural Mountains, from geography and geology to climate and cultural significance."

Introduction
The Caucasus Mountains and the Ural Mountains are two iconic mountain ranges that shape the geography and history of Eurasia. Although both mountain chains play important roles in regional ecosystems, cultures, and economies, they have significant differences that set them apart. In this article, we will explore these differences in depth, comparing the two mountain ranges in terms of geography, climate, biodiversity, historical significance, and more.
Introduction to the Caucasus Mountains
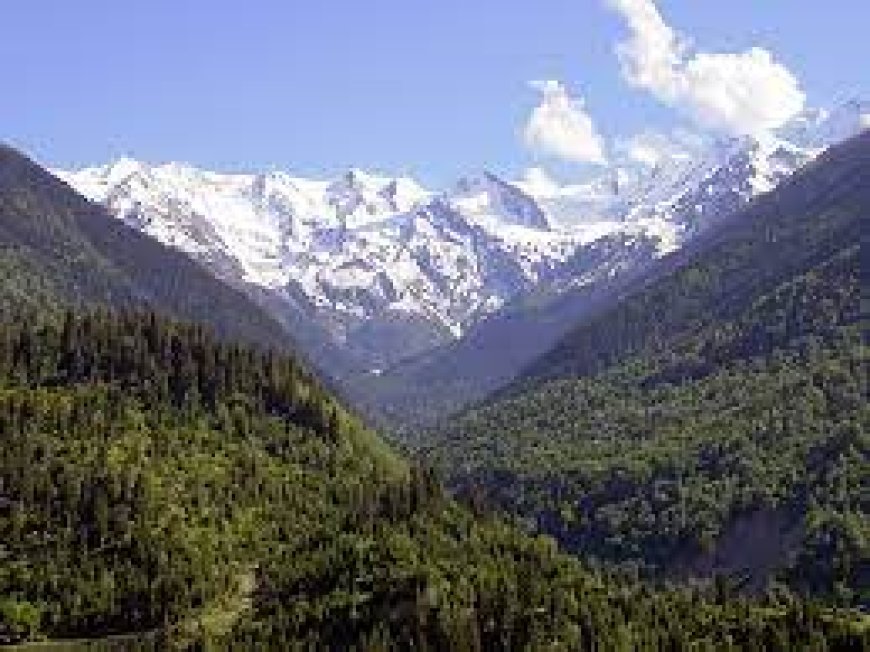
The Caucasus Mountains are located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, stretching across parts of Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. This mountain range is known for its dramatic terrain, which includes towering peaks, deep valleys, and lush forests. It serves as a natural boundary between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, and its peaks are among the highest in Europe and Asia, with Mount Elbrus being the tallest at 5,642 meters (18,510 feet).
Caucasus Mountains(source Wikipedia)
The Caucasus region is a hub of biodiversity and cultural heritage, with numerous ethnic groups calling it home. Over the centuries, the Caucasus has been a crossroads of various empires, including the Persian, Ottoman, and Russian Empires, each leaving a significant imprint on the region’s culture and history.
Introduction to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains, on the other hand, stretch across Russia from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Ural River in the south. Unlike the Caucasus Mountains, the Urals are older and less rugged, characterized by smooth, rolling hills and vast plains. The Ural range is often considered the natural divide between Europe and Asia, marking the boundary between the European and Siberian plains.
Ural Mountain in Russia
While the Ural Mountains do not boast the towering peaks of the Caucasus, they are rich in natural resources, particularly minerals. The Urals have been a significant part of Russia’s industrial development, with mining and metalworking being key economic activities in the region.
Key Differences in Geographical Features
Topography of the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are renowned for their dramatic topography. The range includes steep slopes, jagged peaks, and narrow valleys, making it one of the most geologically active regions in the world. The mountain range is often referred to as the "roof of the world" due to the extreme heights of its peaks, which rise above 5,000 meters (16,404 feet) in many places. The region also has several active volcanoes, adding to its unique landscape.
Topography of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains, in contrast, are much older and have been shaped by millions of years of erosion. As a result, they are lower in elevation, with the highest peak, Mount Narodnaya, reaching only 1,895 meters (6,217 feet). The range is characterized by gently sloping hills and plateaus, rather than the steep cliffs seen in the Caucasus. The Ural Mountains are often described as "rolling hills" rather than rugged peaks.
Climate Comparison: Caucasus vs. Ural
Climate of the Caucasus Mountains
The climate in the Caucasus Mountains is diverse, ranging from subtropical in the lowlands to alpine at higher elevations. Due to the range's great vertical extent, temperatures can vary dramatically. In the valleys, the climate is warm and temperate, while the higher altitudes experience cooler temperatures year-round, with frequent snowfall during the winter months. The region’s varied climate supports a rich diversity of flora and fauna.
Climate of the Ural Mountains
The climate of the Ural Mountains is largely continental, with cold winters and warm summers. The northern parts of the Urals experience severe Arctic conditions, with long, frigid winters and short, cool summers. The southern Urals, however, have a more temperate climate, with milder winters and hotter summers. This climate difference makes the Urals more suitable for large-scale agriculture, unlike the harsh conditions in the higher elevations of the Caucasus.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Unique Ecosystems in the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are known for their remarkable biodiversity, being home to many endemic species. The region’s varied climate and topography support a wide range of ecosystems, from subtropical forests to alpine meadows. Among the species found here are the endangered Caucasian leopard, the Western Caucasian bison, and a variety of endemic plants. The high-altitude ecosystems are also home to unique species of birds and insects.
Biodiversity of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains also host diverse ecosystems, though they differ from those in the Caucasus due to the range's more temperate climate. The region is rich in coniferous forests, which cover much of the northern Urals, while the southern parts are characterized by mixed forests and steppe vegetation. The Urals are home to several species of deer, elk, and bears, as well as numerous smaller mammals and birds.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Ancient Civilizations in the Caucasus
The Caucasus Mountains have been a cradle for human civilization for thousands of years. Ancient kingdoms such as Colchis and Iberia thrived in the region, and the mountains played a pivotal role in the establishment of trade routes between Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The Caucasus was also a center for early Christianity, with several monasteries and churches dotting the landscape.
Historical Importance of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains have long been an important cultural and economic barrier for Russia, acting as the natural divide between Europe and Asia. Historically, the Urals have been a gateway for the movement of peoples and goods between the two continents. The range’s mineral wealth also made it an important region during Russia’s industrialization in the 19th and 20th centuries.
The Role of the Caucasus and Ural Mountains in Geography and Economy
Economic Importance of the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are not only a natural barrier but also a vital region for agriculture, mining, and tourism. The region's rich natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, contribute significantly to the local economy. Additionally, the Caucasus is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors with its stunning landscapes, historic sites, and unique cultures.
Economic Significance of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains are crucial to Russia's industrial sector, particularly in mining and metallurgy. The Urals have been the center of Russia’s metal production for centuries, with vast reserves of iron, coal, and precious metals. The region also plays a vital role in transportation, serving as a corridor for goods and resources moving between Europe and Asia.
Geological Composition and Tectonics
Geological Features of the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are a young mountain range, formed by tectonic activity due to the collision of the African and Eurasian plates. This ongoing tectonic movement results in the region's dramatic landscapes, including numerous faults, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. The Caucasus is rich in minerals, with deposits of coal, oil, and precious stones.
Geology of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains are much older, having formed over 250 million years ago during the Uralian orogeny. The range’s geology is characterized by ancient rocks, such as granite and schist, as well as a wealth of mineral deposits. The Urals are particularly known for their rich mineral resources, which have supported the region’s mining industry for centuries.
Challenges in Conservation and Preservation
Conservation Issues in the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains face significant conservation challenges due to deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat destruction. Efforts are being made to protect the region’s unique biodiversity through national parks and protected areas. However, ongoing conflicts and development pressures remain threats to the region’s ecosystems.
Preservation Challenges in the Ural Mountains
In the Ural Mountains, industrialization has posed significant environmental threats. Mining and logging have led to habitat destruction and pollution, affecting the region’s wildlife and natural resources. Conservation efforts in the Urals are focused on mitigating these impacts through sustainable practices and environmental protection regulations.
Conclusion: Comparing the Significance of Both Mountain Ranges
Both the Caucasus and Ural Mountains are integral to the geography, culture, and economy of Eurasia. While the Caucasus is known for its dramatic landscapes, high peaks, and rich biodiversity, the Ural Mountains stand out for their historical and economic importance, particularly in mining and industry. Understanding the unique features of these mountain ranges helps to appreciate their distinct roles in shaping the surrounding regions.
FAQs
1. What is the highest peak in the Caucasus Mountains?
The highest peak in the Caucasus Mountains is Mount Elbrus, which stands at 5,642 meters (18,510 feet).
2. How are the Caucasus and Ural Mountains different in terms of geography?
The Caucasus Mountains are characterized by steep, rugged peaks and valleys, while the Ural Mountains are older and feature rolling hills and plateaus.
3. What types of animals live in the Caucasus Mountains?
The Caucasus is home to a variety of endemic species, including the Caucasian leopard, Western Caucasian bison, and many rare birds and plants.
4. Which mountain range has more mineral resources?
The Ural Mountains are rich in mineral resources, including iron, coal, and precious metals, making them crucial to Russia's mining industry.
5. What role do the Ural Mountains play in Russian history?
The Ural Mountains have historically served as a natural divide between Europe and Asia, as well as a key region for Russia’s industrial development, particularly in mining and metallurgy.
6. How do the climates of the Caucasus and Ural Mountains differ?
The Caucasus has a diverse climate, ranging from subtropical to alpine, while the Urals experience a continental climate with colder winters and milder summers.